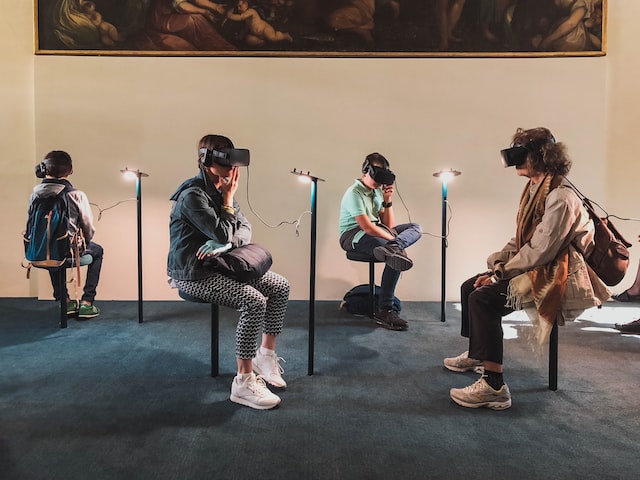
Augmented reality (AR) is making its rounds in almost every sector. Furniture stores are using it to help customers visualize what a couch will look like in their empty living room, and teachers can use it to help students engage with their senses.
“AR can benefit students by making the imaginary more visual, providing context for complex topics”
It’s time to embrace the increased technology used by younger generations and use it to their educational advantage.
What Is AR in the Classroom?
AR allows students to superimpose audio and visual elements onto real environments. They can use the technology to see how big animals would be or what would happen during a particular chemical reaction. The number of AR devices is expected to be around 1.4 billion in 2023, only to keep increasing.
Students actively use more of their senses with AR. Instead of listening to a lecture and optionally taking notes, incorporating AR makes them use their body. Students may stand up and walk around their environment, retaining additional information about the subject matter because the sounds and visuals are more relevant.
Students could use all these tools on smartphones or tablets. Here are some of the most popular applications making AR seamless in classrooms:
- Merge Cube
- Assemblr
- Narrator AR
- Wonderscope
- Grib
- JigSpace
- CoSpaces Edu
These firsthand experiences with materials hold students’ attention, making it easier for educators to teach effectively. About 80% of students are more likely to report to a class that utilizes AR. It attaches to the younger generation by appealing to their sensibilities, creating a unified learning experience with fewer disruptions.
How Does AR Help Students Learn?
Students pursuing higher education need digital literacy. They are highly proficient in operating phones, but it doesn’t necessarily correlate to their mastery of other technological devices. Engaging with AR gives students more opportunities to experiment with new technology, further preparing them for higher education or the programs they will use in their professional life.
Collaboration and student engagement are streamlined with AR. AR provides an avenue to decrease shyness and anxiety for students struggling with team exercises. Technology adds another layer to an otherwise intimate learning experience, potentially forcing students who don’t know each other well to create solutions productively.
Educators could also join in on the adventure, engaging with students in the AR environments as a guide. It could also improve student-teacher relationships, creating a sense of trust and autonomy as they navigate these worlds independently.
Some educators may worry about funding AR materials. However, there is cost-effectiveness to AR that some overlook. Most students have smartphones, making the cost minimal if they download apps on their phones or school-sponsored laptops to complete assignments. However, some students may not own phones, and teachers may need to consider creative solutions to ensure the classroom has equal access. This means fewer dollars spent on crafting supplies and books that sit on shelves collecting dust.
It also helps simplify complex concepts. This could help level the field in classrooms, especially in assisting students with special needs or others with difficulties, such as spatial awareness or motor skills.
“Appealing to different learning styles with AR may help create a stronger foundation for certain subjects so lesson pacing is more consistent”
It can also encourage creativity. The extra stimuli from AR could unlock ideas in students’ minds that a traditional lecture cannot provide. It could let them create interactive presentations or utilize social media in healthy ways to adjust to more beneficial habits.
What Are Ways to Incorporate AR in Lessons?
Envisioning what AR looks like in a classroom is highly individualized, depending on your student makeup and lesson plan priorities. Distilling why you want to incorporate AR will only help students understand concepts better.
You may have a personal resolution to make your classroom more fun. You might also recognize subject areas in your niche that you aren’t as confident in teaching effectively and want to find ways to incorporate AR to supplement those lessons.
Regardless of if you’re teaching in grade school or higher education, there are countless ways, depending on the subject, to incorporate AR:
- Math: AR could supplement textbooks by providing three-dimensional visualizations of geometric concepts, such as shapes, angles or axes.
- Sciences: Students could witness what happens when compounds form, or they can modify molecular structures to create their own reactions — with no potentially dangerous repercussions.
- Engineering: Before building a bridge, students could see if the materials chosen would provide the structural integrity they need.
- History: Certain historical events are becoming more removed from modern generations. AR could help students visualize things they have trouble conceptualizing, like the fall of Rome.
- Medicine: Simulations could assist aspiring surgeons in testing a complicated procedure before trying it on a human.
- Theater: Apps can be used to visualize set designs or lighting setups. This saves programs time and money by not wasting materials that wouldn’t work for the production.
Augmented Reality as a Learning Tool
Digital learning has been normalized in the last couple of years, and educators should accept the benefits of implementing new technologies. Innovations must encourage new and developing minds to stay engaged in learning materials. AR is a prime opportunity to see how well teachers can adapt and maximize the value of education in the modern age.